Massage In SW Florida
Learn about Massage and Health Benefits
Archives
Categories
Recent Articles
- Professional stress and pain relief are just a click away.
- HEALTH BENEFITS OF PAPAYA.
- Our Facebook Page.
- Massage Therapy Benefits Cancer Patients
- Human Anatomy Quiz part 1
- The Health Benefits of Eating Almonds
- Avocados: 10 Nutritional Benefits
- Cancer’s Natural Enemy
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfates Target Arthritis
- Energize Naturally with ENADA
-
No Comments
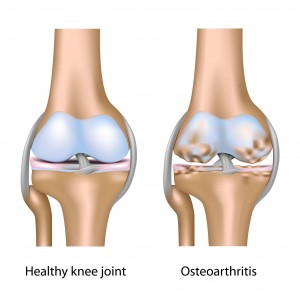 Since the publication of the Arthritis Cure, articles and products touting the benefits of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfates have flooded the American market. But can these substances actually improve arthritis symptoms and is there good science and research to support their use? The answer to both of these questions is yes.
Since the publication of the Arthritis Cure, articles and products touting the benefits of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfates have flooded the American market. But can these substances actually improve arthritis symptoms and is there good science and research to support their use? The answer to both of these questions is yes.
Doctors in Europe and Asia have been using glucosamine and chondroitin sulfates for years to treat osteoarthritis and other joint problems. Numerous studies have shown that these substances are effective in reducing joint pain, swelling and tenderness and improving range of motion. Thousands of patients worldwide have found relief through the use of these ingredients. Despite these positive findings overseas, glucosamine and chondroitin sulfates did not become well known in the US until the publication of the best- seller The Arthritis Cure by Jason Theodosakis, M.D., M.S., M.P.H. In the book, Dr. Theodosakis lays out the scientific basis for the use of these ingredients and the large body of research supporting their use in osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, is a degenerative joint disease that affects approximately 30 million people in the US. NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help manage the pain, but they can have dangerous side effects and drug interactions. Long-term use of the NSAIDS can actually worsen joint damage. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfates, on the other hand, actually address the cause of osteoarthritis and exert a beneficial effect on the disease process itself.
Glucosamine sulfate is a naturally occurring ingredient made up of sugar and an amino acid. It is needed to produce proteoglycans, substances that are essential to the structure and function of cartilage in the joint. Glucosamine sulfate provides the joints with the building blocks needed to repair damage from osteoarthritis. Glucosamine sulfate has been the subject of over 300 scientific investigations including over 20 double-blind studies. These studies have shown that glucosamine sulfate helps to reduce pain and improve joint function in those with osteoarthritis. Results of ten clinical studies show that glucosamine sulfate relieves the symptoms of osteoarthritis at least as effectively as NSAIDS.
Chondroitin sulfate consists of long chains of sugar units. It is a major component of cartilage where it functions to hold in fluid and nutrients. In damaged joints, chondroitin sulfate helps to inhibit cartilage-destroying enzymes. Chondroitin sulfate is also responsible for giving cartilage its sponge-like quality.
As the evidence shows, there is now a better approach to arthritis than simply blocking pain and inflammation with drugs. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate can halt and even reverse the process of arthritic joint damage. These substances are normally found in the body and do not produce any significant side effects. Taking these supplements can actually help the body to repair the damaged joints themselves leading to a reduction in pain and swelling and an increase in mobility.
-
1 Comment
 ENADA is the ONLY patented, stabilized, absorbable oral form of NADH available.
ENADA is the ONLY patented, stabilized, absorbable oral form of NADH available.
NADH is a coenzyme naturally present in all living cells that is necessary for energy production and cellular development. It is also essential to the functioning of the body’s immune system. NADH triggers energy production in all cells by generating ATP, the body’s energy storehouse.
NADH stimulates production of serotonin and other neurotransmitters, which help to improve mental clarity, alertness and concentration. NADH is a powerful antioxidant, and it plays a key role in repairing damage to DNA.
In a recent FDA-approved study conducted at Georgetown Medical Center, CFS patients taking ENADA NADH were four times more likely to improve than those taking a placebo. During a longer follow-up study, it was observed that 73% of the subjects achieved marked improvement over time. This study marked one of the only times the FDA has approved testing of a nutritional supplement for potential medical benefit. Leading CFS doctors and researchers recommend ENADA to increase energy levels and improve symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome. In addition to its positive effects on CFS, ENADA has shown tremendous potential as a natural anti-depressant. In a recent study of 205 patients suffering from depression, all benefited from ENADA. In the study, ENADA was shown to alleviate symptoms of depression such as hopelessness, guilt, sleep disturbances and suicidal thoughts. NADH helps to balance brain chemical such as norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
NADH is a valuable tool in the fight against aging especially age-related mental decline. ENADA NADH can energize aging or degenerative brain cells. Also, its ability as an antioxidant can protect the brain from cellular damage due to free radicals. Studies in Alzheimer’s patients have been very encouraging. ENADA is currently being tested at Georgetown University Medical Center for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease, and in long-term CFS studies.
ENADA is not just for those with chronic disease or age-related illness. It is used by athletes who want to gain an edge and by individuals wanting to naturally and safely increase energy levels.
ENADA is very safe with no side effects. It has no known interaction with prescription medications or other supplements. -
No CommentsWater is the reason your body works the way it does and without water your body would not be able to perform even the simplest functions. When the body can no longer perform theses functions normally, the body begins breaking down and can cause serious health conditions to arise.Some of the most remarkable benefits of hydration are listed below:
- Brain Adequate hydration is important for proper functioning of the brain. When we are well hydrated, brain cells are better supplied with fresh, oxygen-laden blood, and the brain remains alert. Mild dehydration, a 1% to 2% loss in body weight, can impair the ability to concentrate. Loss of more than 2% body weight due to dehydration can affect the brain’s processing abilities and impair short-term memory.
- Cells Hydration in the body is important for transporting carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and other important nutrients and oxygen to the cells. The cells then produce energy for the body to function. Furthermore, hydration facilitates disposal of the waste products of metabolism, enabling the right cellular chemical function.
- Digestive Tract Hydration plays an important role in the digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients from the digestive tract. Water is required to dissolve nutrients so that they may be absorbed into the bloodstream and delivered to the cells. Insufficient hydration will slow the digestive process and chronic poor hydration can lead to constipation.
- Heart Fluids are important for healthy heart function and the correct regulation of water balance is essential to keep blood pressure within the healthy range. Dehydration decreases cardiac output which may lead to increases in heart rate and a fall in blood pressure. The circulatory system delivers a constant supply of oxygen to the brain, muscles and to all other tissues.
- Kidneys An adequate water intake is essential to keep the kidneys working well, helping them to remove waste products and excess nutrients mainly via urine. The kidneys regulate the body’s water levels by increasing or decreasing the flow of urine. The kidneys also work to control normal levels of sodium and other electrolytes. A well-hydrated healthy person’s kidneys filter approximately 180 litres of water each day: clearly most of this has to be reabsorbed to prevent excessive losses from the body.
- Muscles and Joints Water acts as a lubricant for muscles and joints; it helps cushion joints and keeps muscles working properly. Muscles and joints, in addition to the bones, are necessary for us to stand, sit, move and carry out all daily activities. Approximately 70 to 75 percent of the muscle is made up of water. Maintaining the right water balance is essential for optimum muscle function.
- Skin The skin constitutes a defence against pathogenic agents and contributes to preventing the development of infectious and allergic processes. Some people believe that good hydration helps to moisten body tissues and preserve the skin’s elasticity, softness and colouring though this has not been researched adequately.
- Temperature The body water has an important role as a thermoregulator, regulating the overall body temperature by helping dissipate heat. If the body becomes too hot, water is lost through sweat and the evaporation of this sweat from the skin surface removes heat from the body. Sweating is the most effective way that the body prevents itself from overheating.
How much water do you need?Every day you lose water through your breath, perspiration, urine and bowel movementsThe Institute of Medicine determined that an adequate intake for men is roughly 3 liters (about 13 cups) of total beverages a day and for women is 2.2 liters (about 9 cups) of total beverages a day.You may need to modify your total fluid intake depending on how active you are, the climate you live in, your health condition and if you are pregnant or breast-feeding.- Exercise. If you exercise or engage in any activity that makes you sweat, you need to drink extra water to compensate for the fluid loss. An extra 400 to 600 milliliters (about 1.5 to 2.5 cups) of water should suffice for short bouts of exercise, but intense exercise lasting more than an hour (for example, running a marathon) requires more fluid intake. How much additional fluid you need depends on how much you sweat during exercise, and the duration and type of exercise.
- Climate. Hot or humid weather can make you sweat and requires additional intake of fluid. Heated indoor air also can cause your skin to lose moisture during wintertime. Further, altitudes greater than 8,200 feet (2,500 meters) may trigger increased urination and more rapid breathing, which use up more of your fluid reserves.
- Illnesses or health conditions. When you have fever, vomiting or diarrhea, your body loses additional fluids. In these cases, you should drink more water. In some cases, your doctor may recommend oral rehydration solutions, such as Gatorade, Powerade or CeraLyte. Also, you may need increased fluid intake if you develop certain conditions, including bladder infections or urinary tract stones. On the other hand, some conditions such as heart failure and some types of kidney, liver and adrenal diseases may impair excretion of water and even require that you limit your fluid intake.
- Pregnancy or breast-feeding. Women who are expecting or breast-feeding need additional fluids to stay hydrated. Large amounts of fluid are used especially when nursing. The Institute of Medicine recommends that pregnant women drink 2.3 liters (about 10 cups) of fluids daily and women who breast-feed consume 3.1 liters (about 13 cups) of fluids a day.
Recognizing Dehydration:
Here are some of the symptoms that you need more water:
- Dark Urine – Dark Yellow or Orange in Color: Urine is generally pale yellow to clear when you have sufficient water intake. Dark color or strong smell indicates that you need to drink more water.
- Dry Skin: Skin is the largest body organ and requires its share of water.
- Thirst: Thirst is the most obvious sign that you are already dehydrated. It is always a good practice to drink more water when your are not thirsty, do not wait until you are thirsty. But thirst is not always an adequate gauge of your body’s need for fluid replenishment. The older you are, the less you are able to sense that you are thirsty.
- Hunger: Most people mistake hunger for the indication to eat more, whereas in actual fact, they may be dehydrated. So before you have your meal, grab a glass of water.
- Fatigue: Water is a source of energy and gives you a boost in energy
Common Beverage Substitutions Lead to DehydrationIt is true that beverages such as tea, coffee, wine, beer, soft drinks, sports drinks and juices contain water, but they also contain caffeine, alcohol, sugar, artificial sweeteners or other chemicals that act as strong dehydrators. The more of these beverages you consume, the more dehydrated your body becomes because the effects they create in the body are exactly opposite the ones that are produced by water. Beverages containing caffeine, for example, trigger stress responses that at first have strong diuretic effects, leading to increased urination. Beverages with added sugar drastically raise blood sugar levels. Any beverage that provokes such a response coerces the body to give up large quantities of water. Regular consumption of such beverages results in chronic dehydration, which plays a part in every toxicity crisis (the body’s effort to rid itself of accumulated toxins). -
1 CommentResearchers at Barts and The London School of Medicine demonstrated that drinking two cups of beetroot juice daily significantly reduced blood pressure in healthy volunteers.The secret is the nitrate in the beetroot juice, which is responsible for lowering the volunteers’ blood pressure.In the human body, nitrate is converted to nitric oxide, a substance that is known for its ability to dilate blood vessels and subsequently reduce blood pressure. The human
 body produces nitric oxide naturally. Unfortunately, nitric oxide production declines progressively with age.Among the study participants, blood pressure fell within just one hour of drinking the beetroot juice, with the greatest drop occurring three to four hours following consumption. The blood pressure-lowering effects continued for up to 24 hours afterward.Recently, however, some scientists have begun investigating the roles played by other plant compounds, particularly nitrate. Nitrate occurs naturally in many vegetables, including spinach, cabbage, radishes and, of course, beets.
body produces nitric oxide naturally. Unfortunately, nitric oxide production declines progressively with age.Among the study participants, blood pressure fell within just one hour of drinking the beetroot juice, with the greatest drop occurring three to four hours following consumption. The blood pressure-lowering effects continued for up to 24 hours afterward.Recently, however, some scientists have begun investigating the roles played by other plant compounds, particularly nitrate. Nitrate occurs naturally in many vegetables, including spinach, cabbage, radishes and, of course, beets.
Just make sure you take into account the extra calories and sugar. A two-cup serving of beetroot juice contains around 200 calories and 50 grams of carbohydrates. If you don’t adjust your daily caloric intake, adding two cups of the juice daily could lead to a weight gain of about a pound and a half a month, which could potentially offset the beetroot-derived cardiovascular benefits.

